Why Threat Modeling is a Must for Secure Apps and AI
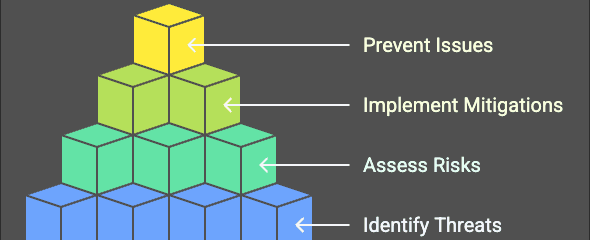
What is Threat Modeling?
Threat modeling is a way to find and fix security risks in a system before they become big problems. It helps teams think about possible threats early so they can stop them before they happen.
OWASP describes threat modeling as a process that helps people find security risks in an application and fix them (OWASP Threat Modeling Project). It’s an important part of designing secure software so that security is built in from the start.
Why is Threat Modeling Important for Businesses?
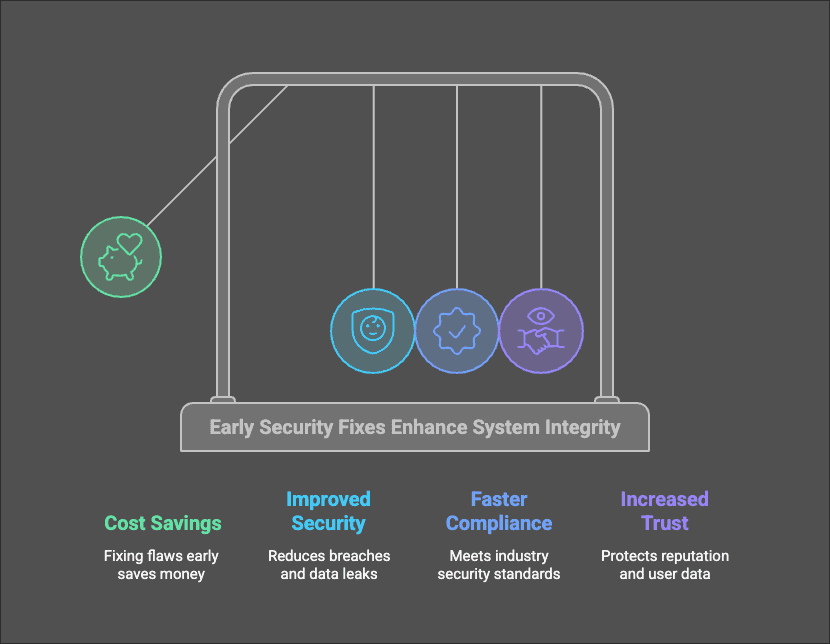
Modern apps are complicated and use many different tools and services. This makes them more vulnerable to attacks. OWASP research shows that businesses implementing threat modeling experience:
How to Carry Out a Threat Modeling Session Today
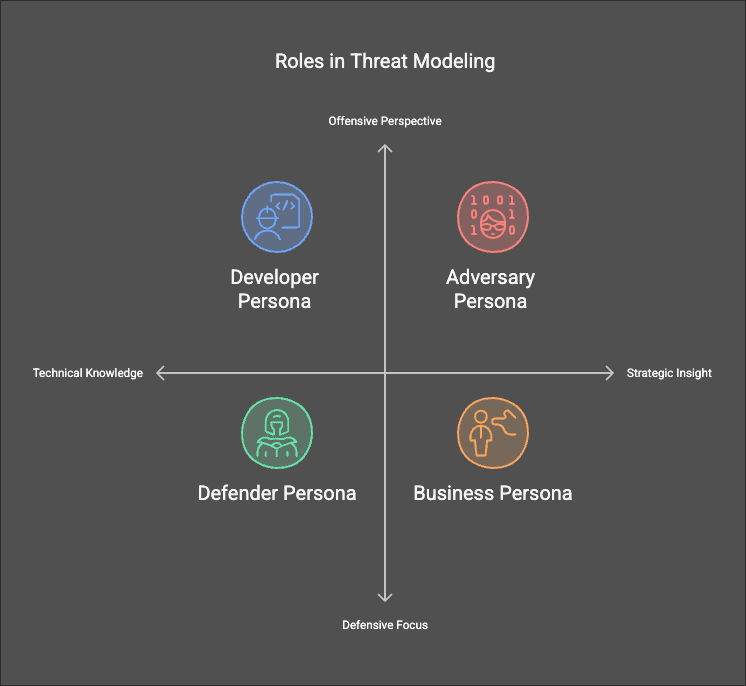
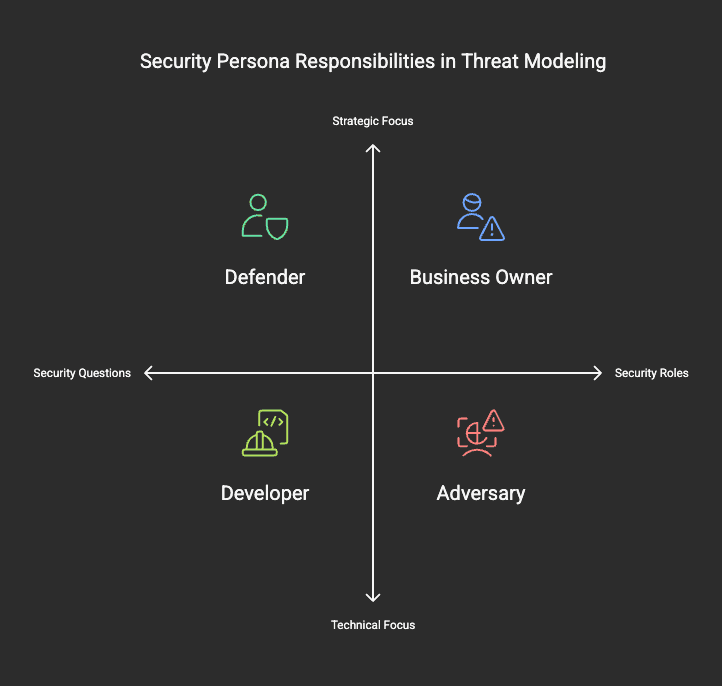
A successful threat modeling session brings together different perspectives. The AppSec SME (Application Security Subject Matter Expert) facilitates discussions with multiple personas:
- Business Persona – Understands business goals and risks.
- Developer Persona – Knows the system architecture and code.
- Defender Persona – Focuses on protecting the system from attacks.
- Adversary Persona – Thinks like an attacker to identify potential weaknesses.
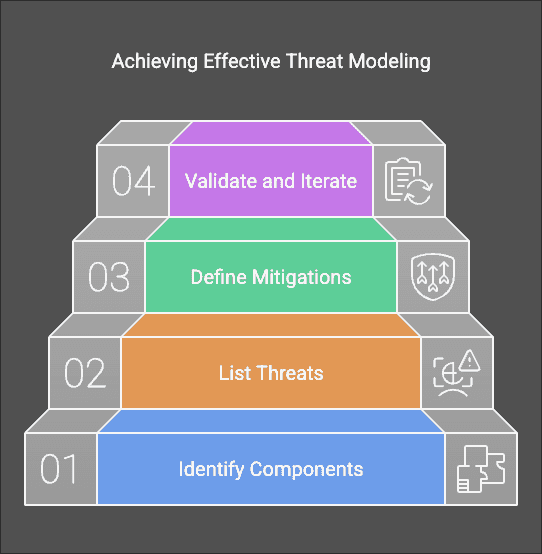
A session typically follows these steps:
- Identify what is being built – Create system diagrams and identify key components.
- List potential threats – Use STRIDE or other models to classify risks.
- Define mitigations – Plan security controls for each identified threat.
- Validate and iterate – Review the threat model regularly as the system evolves.
Drive Consistency in Threat Modeling
Threat modeling works best when it is consistent and repeatable. Three key factors help maintain quality:
1. Methodology
- Re-use existing threat models to save time.
- Estimate effort required for security tasks.
2. Format
- Learn from existing threat models.
- Work asynchronously using shared documentation.
3. Decomposition
- Break down systems into smaller parts for detailed analysis.
- Use past models to guide new assessments.
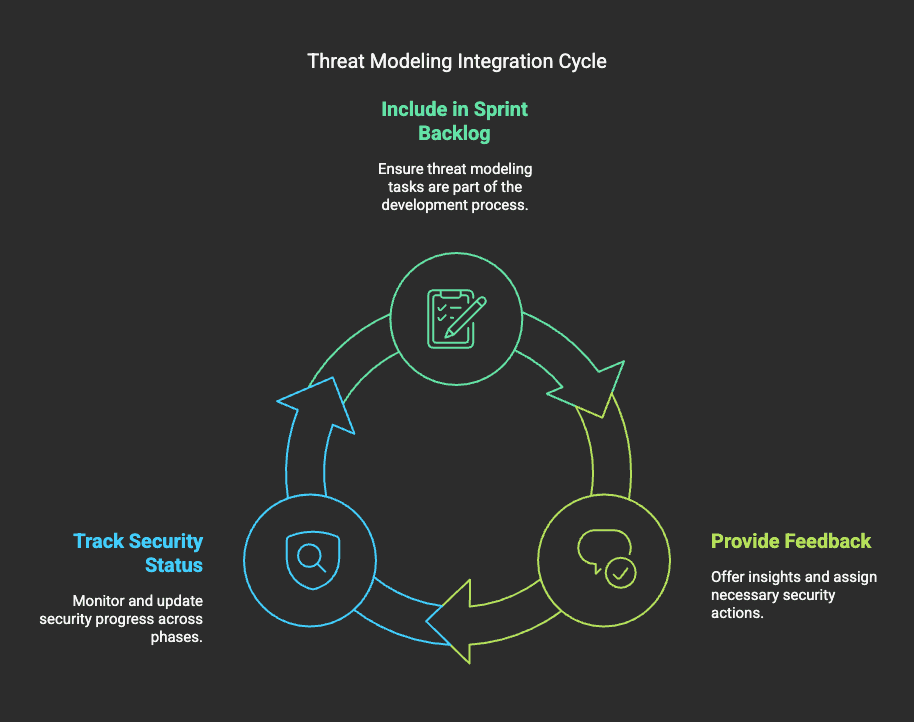
Integrate with Your SDLC and Tooling
For threat modeling to be effective, it must be embedded in the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). This requires:
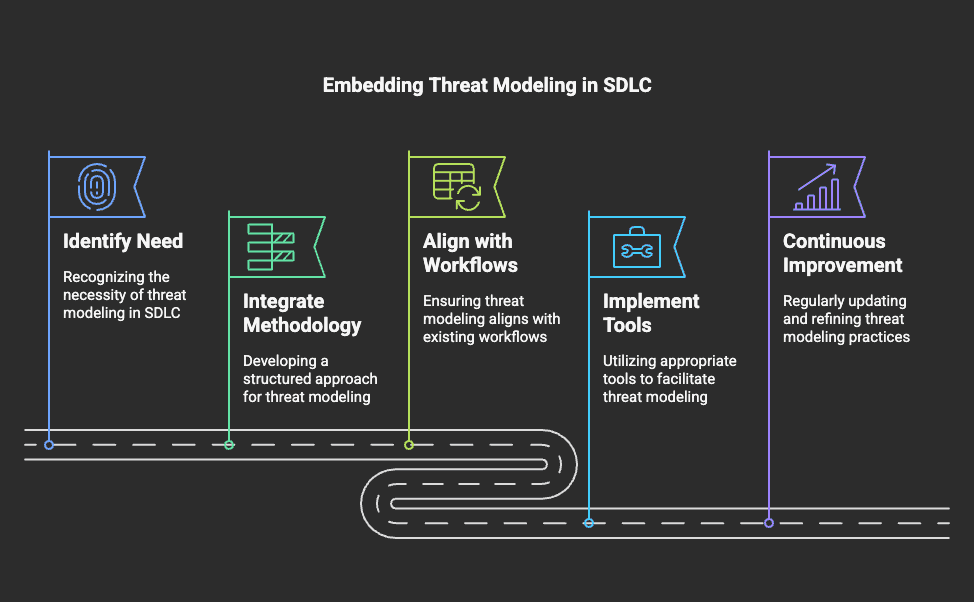
Work Management Tools
- Include threat modeling in the sprint backlog.
- Provide feedback and assign security actions.
- Track security status across development phases.
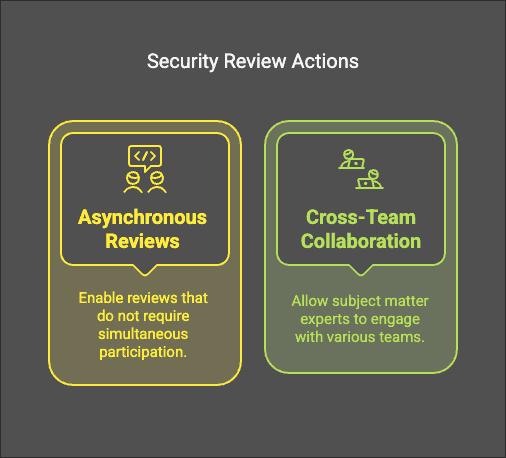
Collaboration Tools
- Enable asynchronous security reviews.
- Allow AppSec SMEs to work across multiple teams.
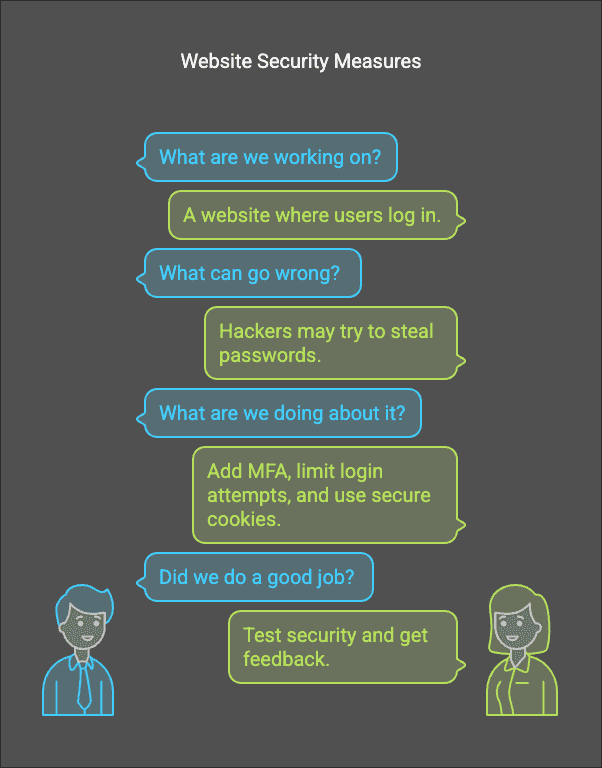
Example: Securing a Web Login System
- What are we working on? A website where users log in.
- What can go wrong? Hackers may try to steal passwords.
- What are we doing about it? Add MFA, limit login attempts, and use secure cookies.
- Did we do a good job? Test security and get feedback.
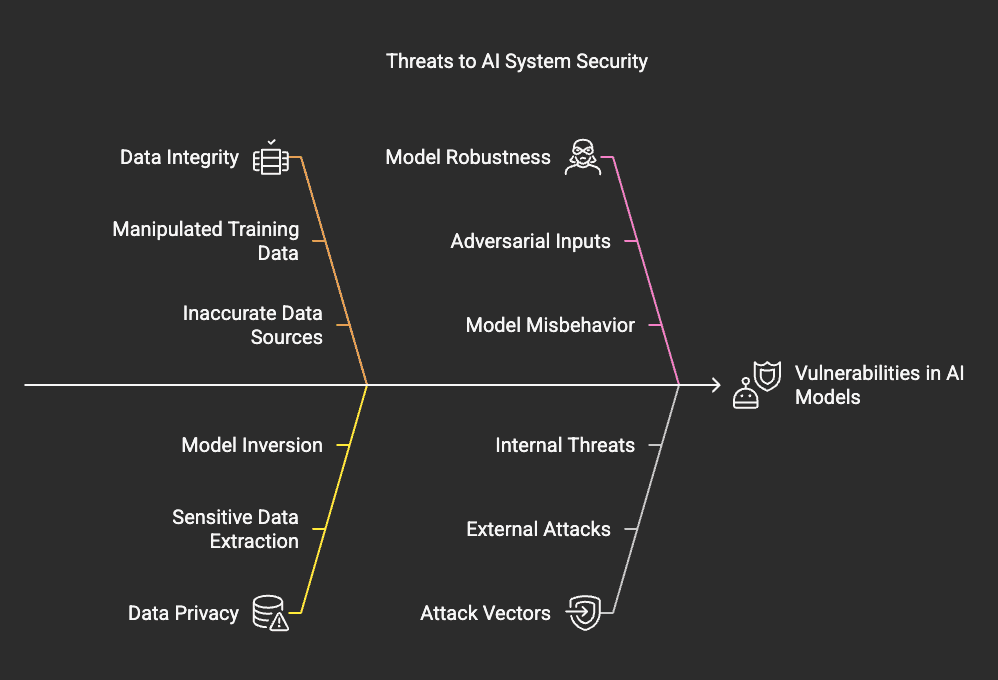
How Threat Modeling Helps AI Systems
As AI becomes more common, securing AI models is a major concern. AI systems are vulnerable to:
- Data Poisoning – Attackers manipulate training data to make AI models behave incorrectly.
- Model Inversion Attacks – Hackers extract sensitive data from AI models.
- Adversarial Attacks – Attackers trick AI models with specially designed inputs.
Using threat modeling for AI ensures:
- Secure training and validation processes.
- Protection against AI model tampering.
- Compliance with AI security guidelines like OWASP Top 10 for AI.
For more AI security details, read Threat Modeling for AI Systems (AWS).
Threat Modeling for AWS Vehicle Fleet Management System
Introduction
Let’s imagine we’re building a Vehicle Fleet Management System that allows fleet managers to efficiently register and manage their vehicles while ensuring data security and system integrity.
This system enables vehicle registration, ownership association, and secure access control using AWS services.
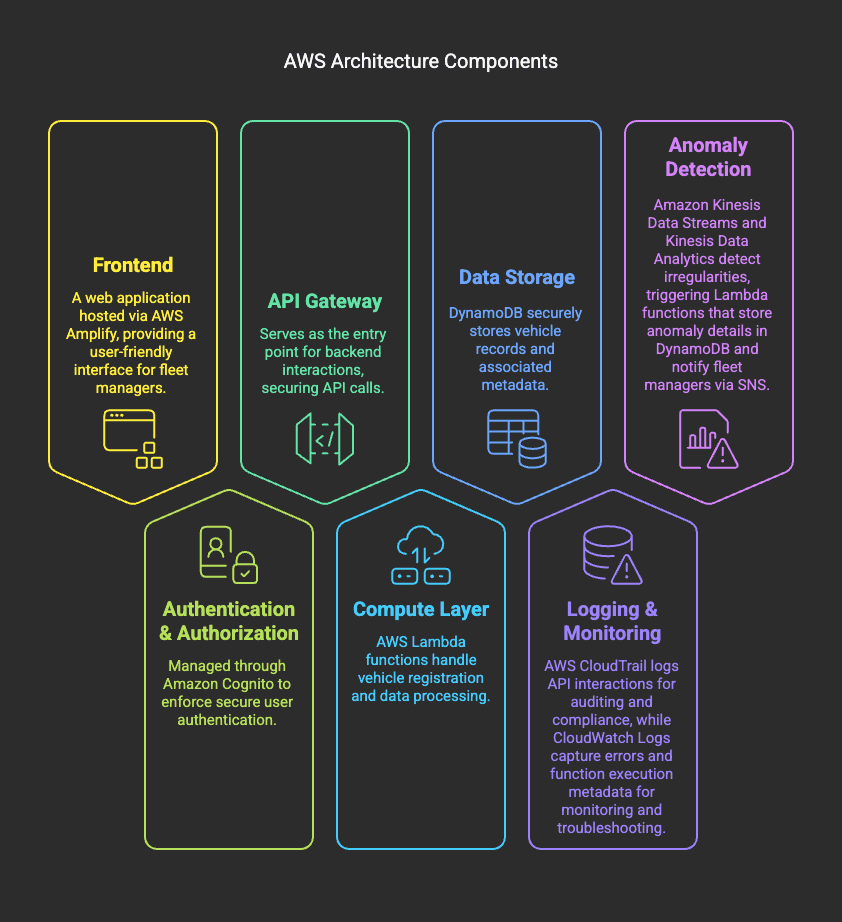
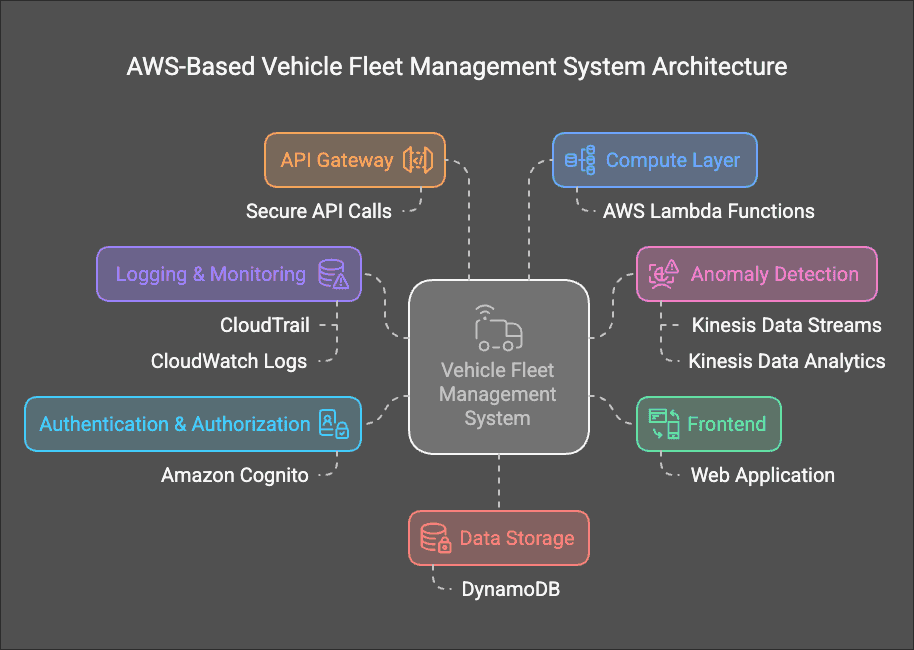
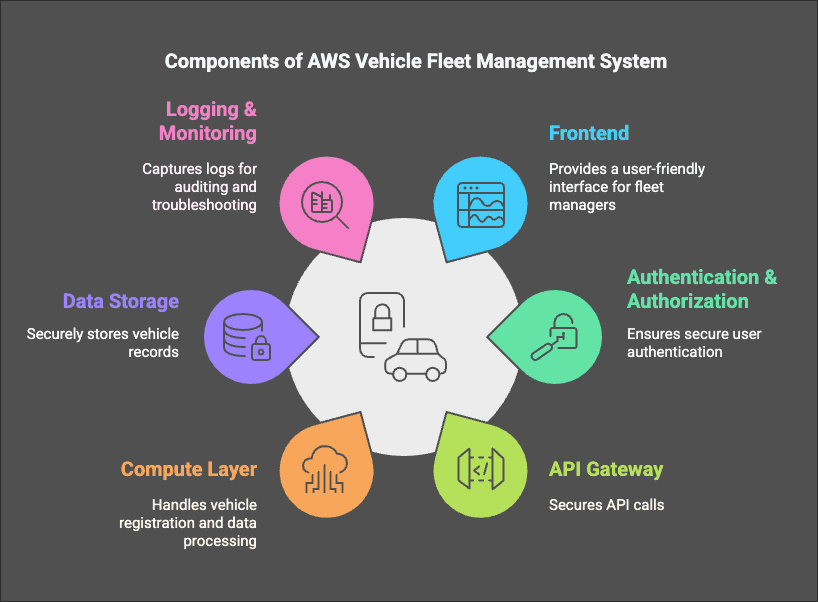
The system is designed with the following architecture:
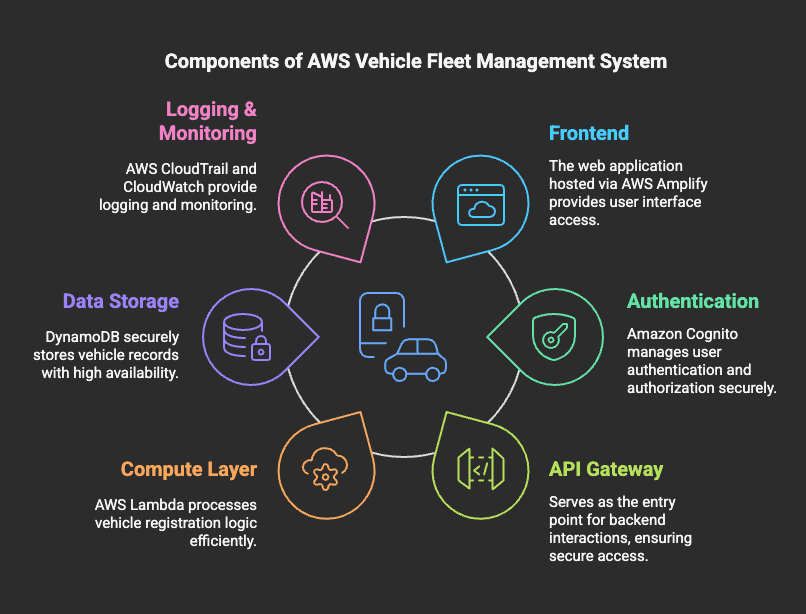
System Components
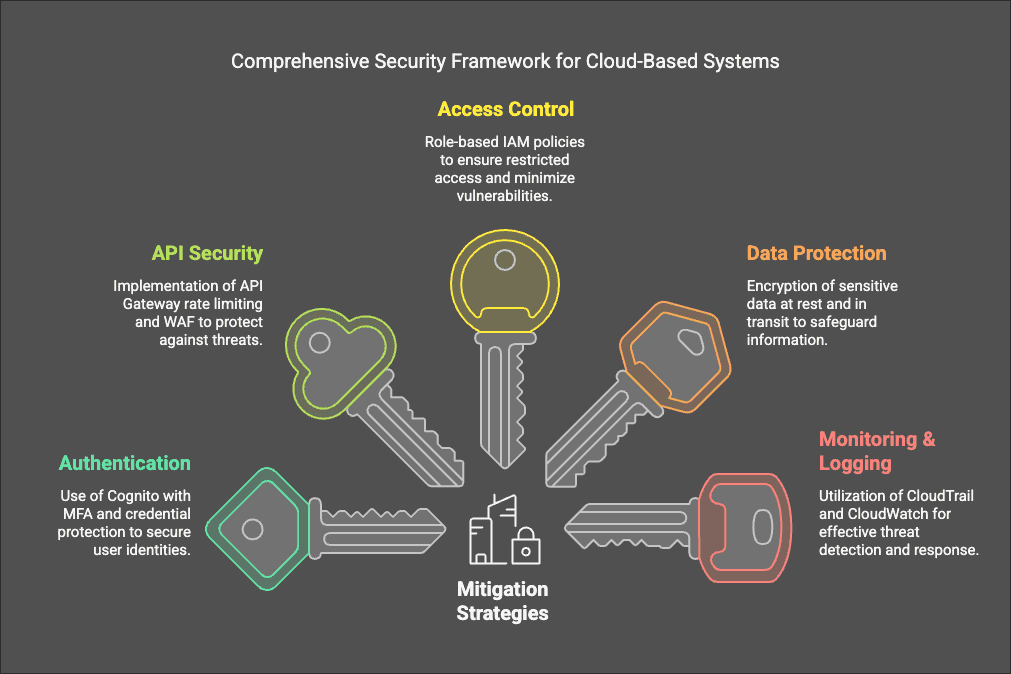
- Frontend: Web application hosted via AWS Amplify
- Authentication & Authorization: Managed through Amazon Cognito
- API Gateway: Serves as an entry point for backend interactions
- Compute Layer: AWS Lambda for processing vehicle registration logic
- Data Storage: DynamoDB for securely storing vehicle records
- Logging & Monitoring: AWS CloudTrail (metadata logs) and CloudWatch (error and execution logs)
- Anomaly Detection: Kinesis Data Streams & Analytics, Lambda, and SNS for monitoring and alerting
Data Flows
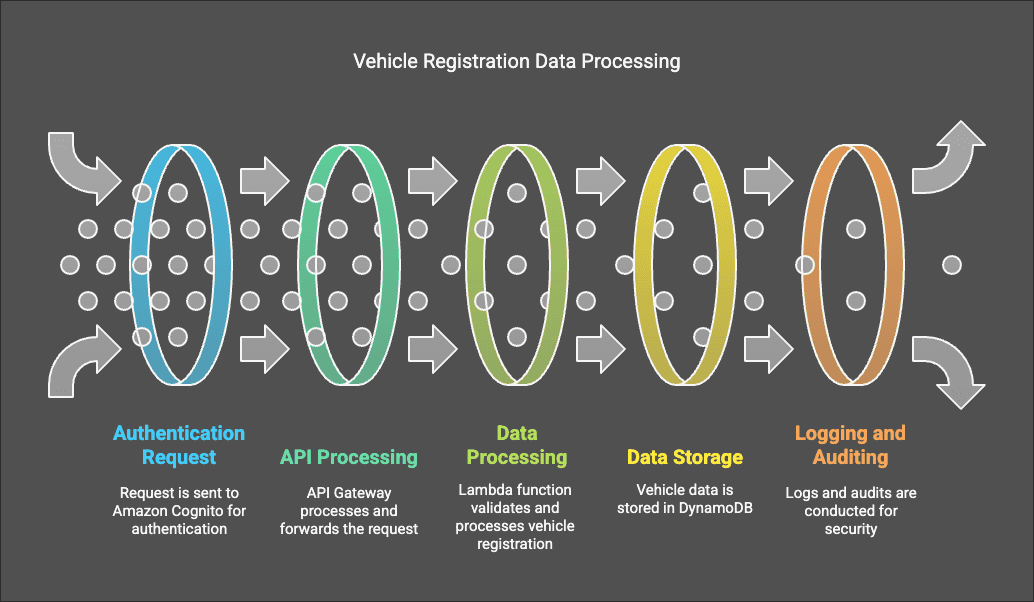
Vehicle Registration Layers
- User accesses the web application via AWS Amplify.
- Authentication request is sent to Amazon Cognito.
- API Gateway processes the request and forwards it to Lambda.
- Lambda function validates and processes the vehicle registration.
- Vehicle data is stored in DynamoDB.
- Error logs and execution metadata are recorded in CloudWatch Logs.
- CloudTrail captures API interactions for auditing.
- CloudTrail logs are analyzed for security threats.
Possible Attack Scenarios & Mitigations
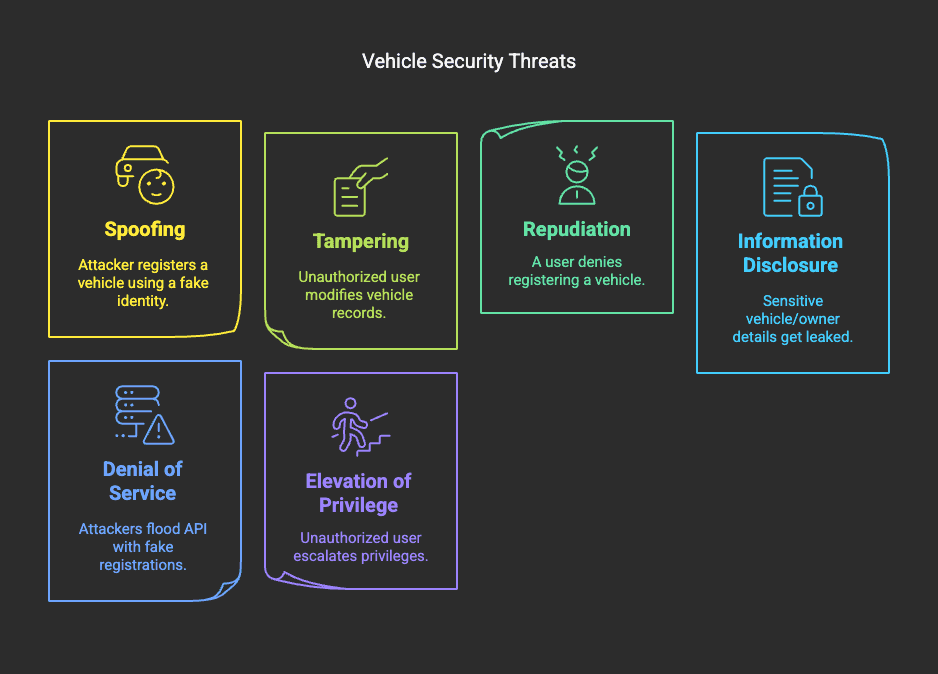
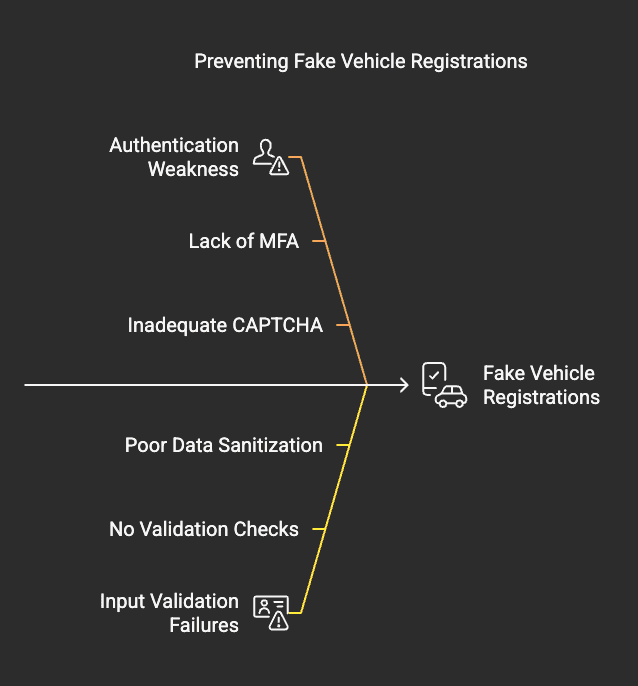
Case 1: Fake Vehicle Registration
- Scenario: An attacker attempts to register vehicles using fake or stolen credentials.
- Mitigation: Enforce strong authentication via Amazon Cognito MFA & CAPTCHA.
- Mitigation: Implement input validation to ensure valid registration details.
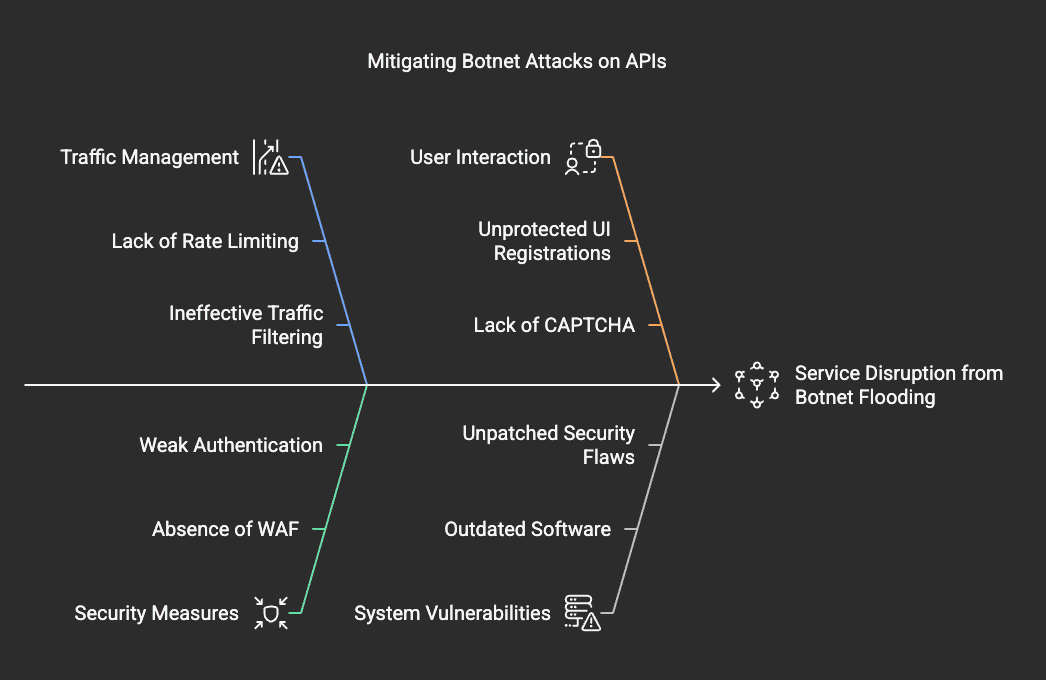
Case 2: Mass API Requests (DoS Attack)
- Scenario: A botnet floods the API with registration requests, causing service disruption.
- Mitigation: Enable API Gateway rate limiting and AWS WAF to filter bad traffic.
- Mitigation: Implement reCAPTCHA for UI-based registrations.
Case 3: Unauthorized Data Access
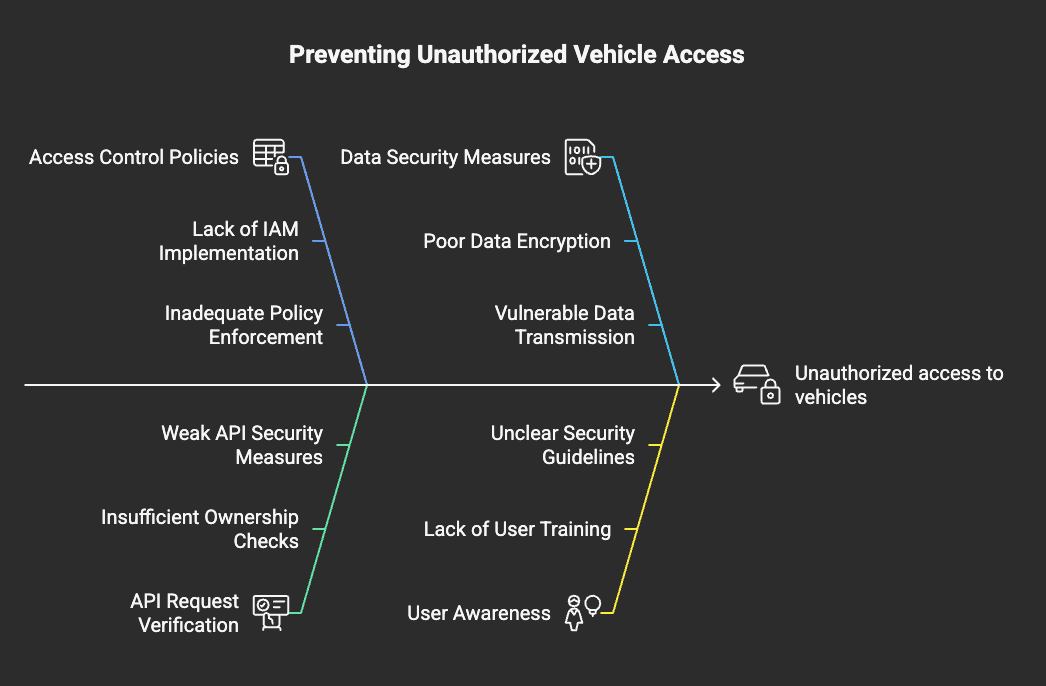
- Scenario: A user gains access to vehicles they do not own.
- Mitigation: Implement IAM-based access control policies to restrict data access.
- Mitigation: Verify ownership before processing API requests.
Case 4: Sensitive Data Exposure
- Scenario: Error messages expose internal database details.
- Mitigation: Use generic error messages that do not disclose database structure.
- Mitigation: Secure logs with IAM permissions to prevent unauthorized access.

Security Personas and Questions
PersonaSecurity QuestionsAdversary (Attacker) Can I register a fake vehicle? Can I access other users’ data?
Defender (Security Engineer) Are authentication and access control strong enough?
Business Owner Will security measures impact user experience?
Developer Are security best practices implemented in API and database interactions?
Mitigation Strategies
What Next? (Security Review Process)
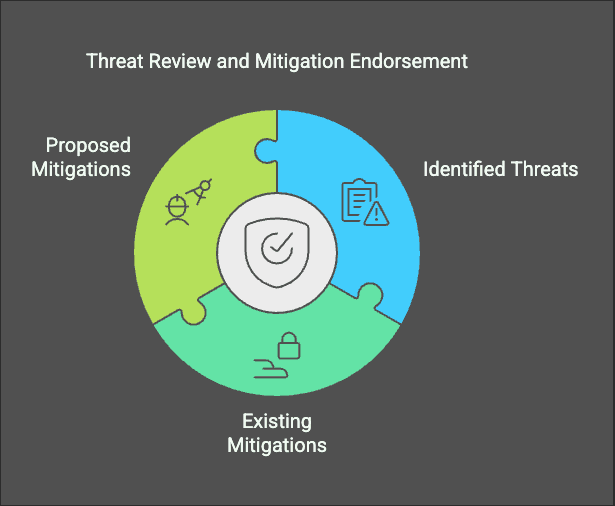
AppSec SME Persona
Reviews and endorses:
- Identified threats
- Existing & proposed mitigations
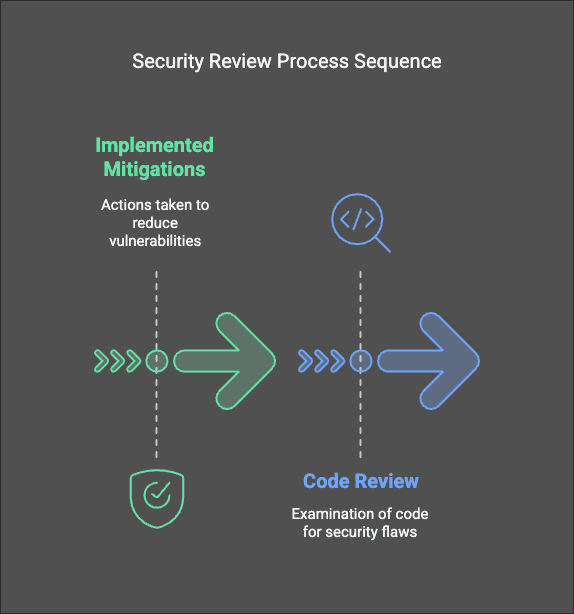
Developer Persona
Delivers:
- Implemented mitigations
- Code review
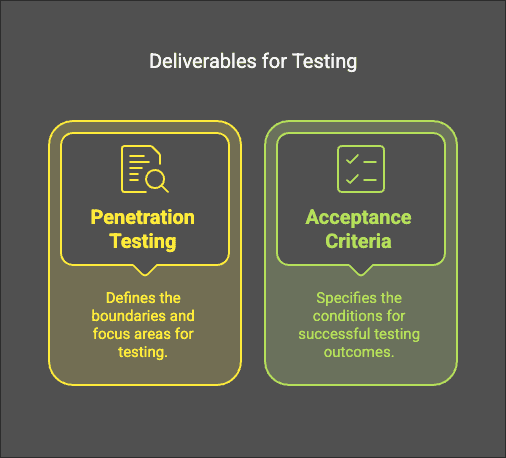
AppSec SME Persona
Sets deliverables:
- Penetration testing scope
- Acceptance criteria
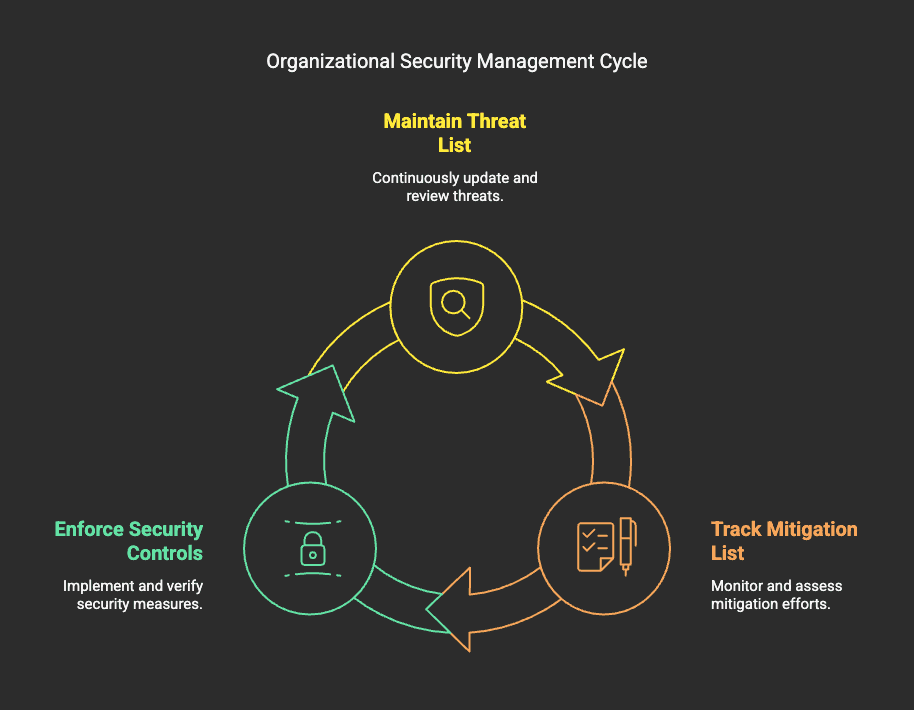
Scaling Organizationally
To ensure security across multiple teams and projects, the organization must:
- Maintain an Organizational Threat List.
- Track an Organizational Mitigation List.
- Enforce Baseline Security Controls.
Moving Forward: Preventing Analysis Paralysis
To avoid overthinking security risks and delaying deployments:
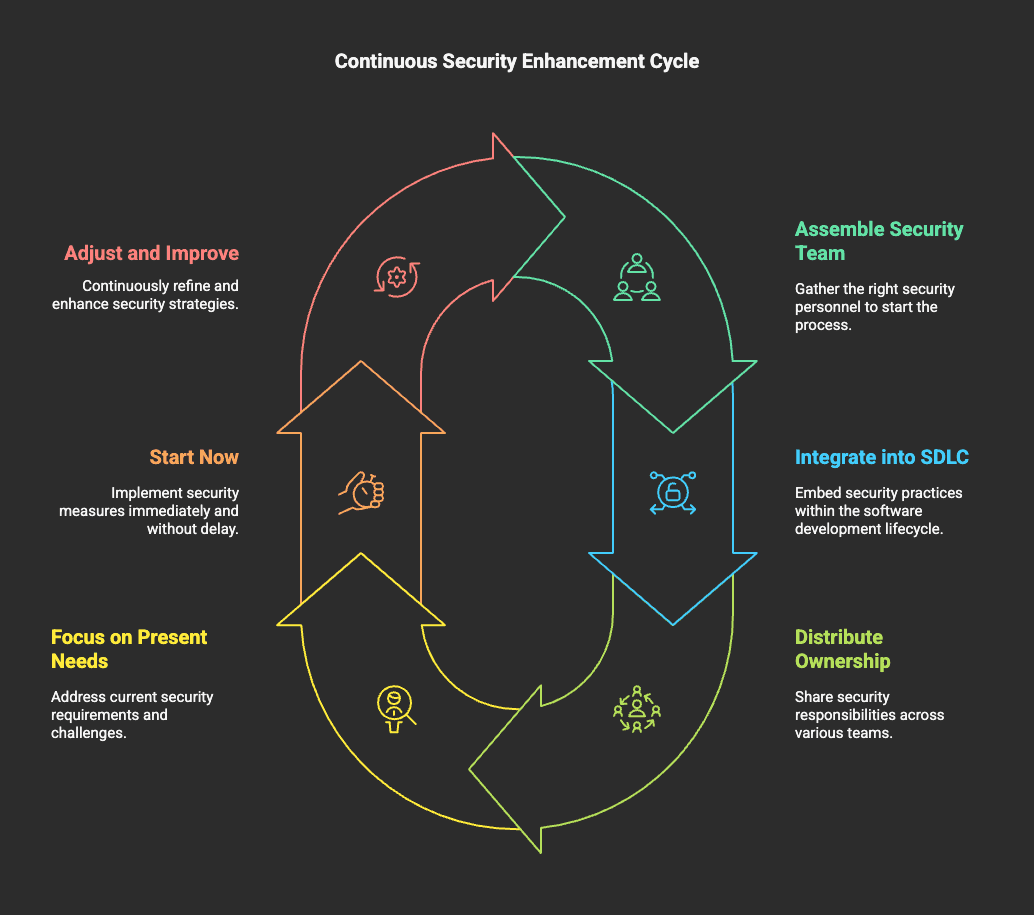
Setup for success:
- Assemble the right security team.
- Integrate security into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
- Distribute security ownership across teams.
Focus on the present: Prioritize current security needs instead of past issues.
Start now: Adjust, iterate, and improve security continuously.
Final Thoughts
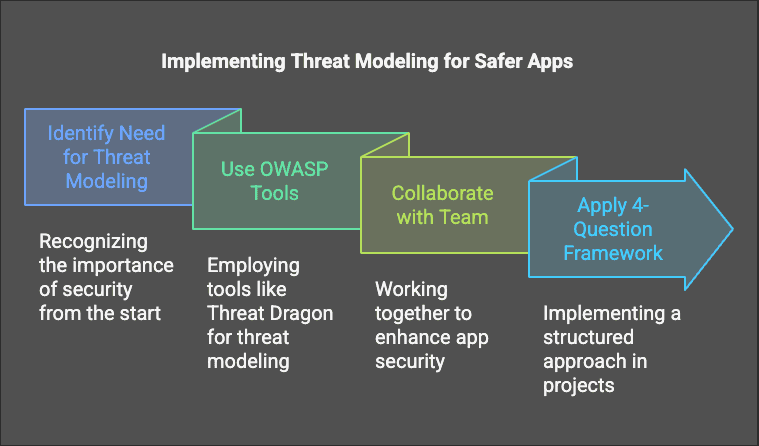
Threat modeling helps build safer apps by thinking about security from the start. It’s a simple process that can prevent serious problems later.
To get started, use OWASP tools like Threat Dragon (OWASP Threat Dragon) and work with your team to improve security.
If you want to apply threat modeling right away, try the 4-Question Framework in your next project!
Keep learning and experimenting (1% growth - Kaizen-style improvement)
- OWASP Threat Modeling
- Threat Modeling Manifesto
- Threat Modeling for AI Systems (AWS)
- AWS Security Blog on Threat Modeling
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Legal Stuff

